CYBERSECURITY A-Z
What Is Security Automation?
Security automation refers to the use of technology – including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) – to perform repetitive security tasks without human intervention. It streamlines workflows, reduces response times, and minimizes errors by handling tasks, such as detection, incident response, and policy enforcement automatically. By reducing the reliance on manual efforts, security automation helps organizations keep pace with evolving threats and the increasing complexity of modern IT environments. Moreover, organizations using security AI and automation lowered breach-related costs by an average of $2.2 million compared to organizations that did not.[i]
Why Is Security Automation Important?
Security operations center (SOC) teams cannot afford to rely solely on manual security processes. Manual security operations struggle to keep pace with increasing threats, compliance requirements, and digital transformation. This happens because organizations have traditionally relied on manually scanning for breaches, investigating threats, and responding to security incidents. Such a manual approach is not only time-consuming, but also overwhelming. Security teams face a deluge of alerts, many of which are false positives. The sheer volume of incidents can lead to alert fatigue, causing security analysts to miss real threats, increasing the risk of breaches.
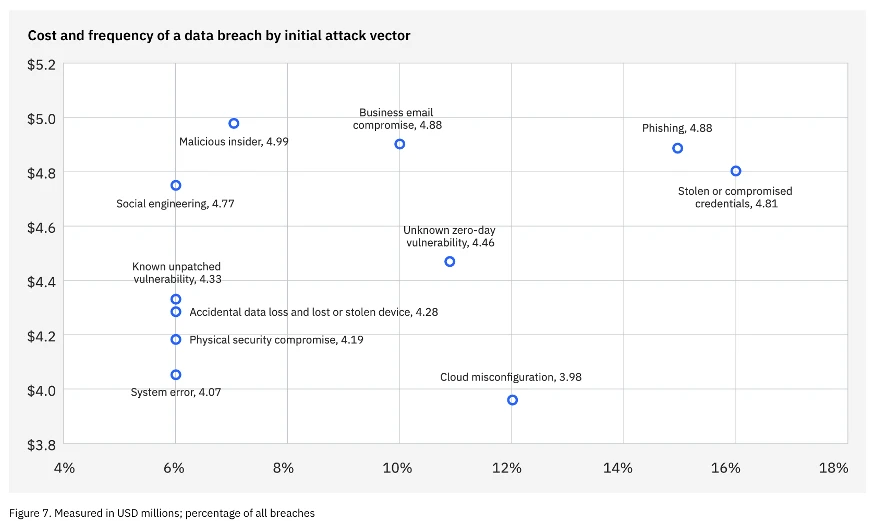
Source: IBM, Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024
Organizations face numerous security challenges that make manual security operations a losing proposition:
- Exploding [Link to glossary page] attack surface – The surge in connected devices—especially IoT and OT—has significantly expanded the attack surface. These assets weren’t built for traditional IT security, like patching, leaving massive visibility gaps and blind spots that distort risk assessments.
- Evolving threats – Forescout observed 900 million attacks in the 2024 threat landscape—up 114% from last year’s 420 million attacks. Cybercriminals aren’t just deploying ransomware – they’re running full-fledged extortion businesses. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operations helped attackers hit multiple organizations at once, crippling entire industries in a single move.
- IT/OT convergence – Industrial digitalization demands IT and OT integration, but weak segmentation allows threats to move unchecked. While many organizations assume that IT and OT are still siloed, the reality is different, and bad actors exploit these overlooked vulnerabilities.
- Siloed security tools – Most organizations juggle dozens of stand-alone security products that don’t talk to each other. This makes it hard for security teams to gain the context they need to coordinate responses.
- Alert fatigue – Security teams receive so many alerts that they become desensitized to them, particularly when the overwhelming volume of alerts are false positives. Add in the uncategorized, unranked nature of alerts, and teams find it difficult to pinpoint true risks and prioritize responses to them.
- Alerts without action – Too many security tools stop at detection. As a result, SOC teams constantly tell Forescout that their tools generate alerts but fail to fix anything. Identifying threats is a good start. But automating threat mitigation is the real game-changer.
- No single source of truth – Troubleshooting a security issue typically requires accessing multiple consoles, piecing together logs, and coordinating across teams. Yet, most tools leave huge gaps in visibility, especially for mobile and BYOD devices.
Together, these challenges prolong critical security response metrics, specifically mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR).
How Security Automation Works
Security automation integrates various cybersecurity tools and technologies to improve an organization’s detection, response, and compliance enforcement. The process typically involves four key stages:
Stage #1: Threat Detection and Analysis
Security automation tools continuously monitor network traffic, logs, endpoints, and applications for suspicious behavior, anomalies, and known attack patterns. This includes:
- AI-driven anomaly detection – Identifies unusual activities that may indicate an attack.
- Threat intelligence integration – Uses global threat hunting and vulnerability databases to detect malicious IPs, domains, and signatures.
- Log analysis – Examines log files to uncover security incidents.
Stage #2: Incident Response and Mitigation
Once a threat is detected, automatic workflows trigger predefined response actions to contain and mitigate the attack. Examples include:
- Isolating compromised endpoints to prevent malware from spreading.
- Blocking malicious IP addresses in firewalls and intrusion prevention systems.
- Quarantining infected files to minimize damage from ransomware.
- Resetting compromised user credentials to prevent unauthorized access.
Stage #3: Compliance and Policy Enforcement
Security automation ensures that organizations comply with industry regulations, such as ISO 27001, GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST. It does this by:
- Automating security audits to track compliance with security policies.
- Enforcing access controls to limit privileged access to sensitive data.
- Monitoring regulatory changes and adapting security policies accordingly.
Stage #4: Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
As cyber threats constantly evolve, security automation must continuously learn, adapt, and refine its response strategies. This involves:
- Machine learning models that improve accuracy over time.
- Security playbooks that update automatically to counter new threats.
- Real-time analytics dashboards that provide visibility into actions.
Combined, these capabilities dramatically shorten MTTD and MTTR.
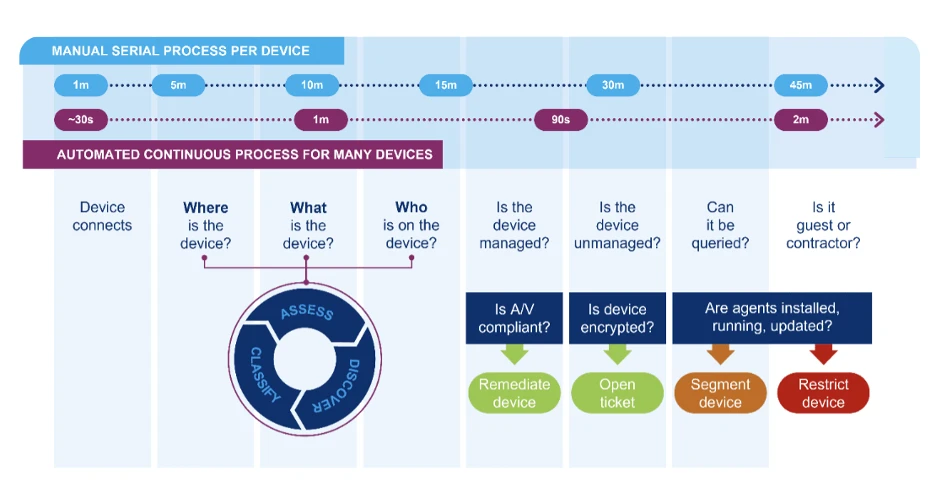
Source: Forescout
Key Benefits
Following are the five key benefits of security automation.
- Faster incident response
Security automation dramatically reduces the time between detection and response. Instead of waiting for manual intervention, systems respond instantly to threats to minimize damage.
- Increased efficiency and productivity
Automation eliminates repetitive security tasks, allowing security teams to focus on more complex, high-value investigations. This also reduces burnout and human error, leading to better overall security operations.
- Enhanced threat intelligence
By integrating real-time threat intelligence feeds, security automation tools continuously update their defenses, making them more effective at blocking emerging threats.
- Cost savings and scalability
With cybersecurity talent shortages and rising attack frequency, organizations must find cost-effective solutions. Security automation helps businesses to scale their security operations without constantly expanding their teams.
- Stronger compliance and governance
Automated security processes ensure that compliance policies are consistently enforced across all systems, reducing the risk of regulatory penalties and data breaches.
Security Automation vs. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response
While security automation is a broad term, it is often discussed alongside [LINK to SOAR glossary page] Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) . The two concepts are related but distinct:
- Security Automation refers to the ability to execute security tasks automatically, such as isolating compromised endpoints, updating rules, or analyzing security logs.
- Security Orchestration is the coordination of security tools, processes, and workflows to ensure seamless communication and efficiency.
- SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) combines both automation and orchestration, enabling organizations to automate responses to threats, streamline processes, and enhance decision-making with integrated intelligence.
In essence, security automation is a foundational component of SOAR, but it doesn’t necessarily involve orchestration and response strategies.
Signs Your Organization Needs Security Automation
Security automation has become a necessity for organizations struggling with mounting security challenges. Here are some telltale signs:
- Rising security breaches – The average breach cost $4.88 million in 2024 – up 10% from the previous year.[i] Just one major cyberattack could have devastating financial consequences. By detecting and mitigating threats faster, security automation helps to reduce the risk of costly incidents.
- Slow incident detect and response times – If your MTTD and MTTR are lagging, your current security framework needs a boost. Automating incident response accelerates detection, containment, and recovery, keeping threats from spreading.
- Struggling with compliance – Keeping up with evolving security regulations and policies can be overwhelming. Security automation ensures compliance by enforcing policies consistently and reducing the risk of human error.
- Drowning in false positives – If your security team is spending too much time on false alarms and not enough on real threats, automation can help filter out the noise. By refining alert accuracy, automation ensures analysts focus on what truly matters.
- Overwhelmed security teams – If your SOC team is battling alert fatigue, bogged down by repetitive manual tasks, or struggling to scale defenses, it’s time to implement automation. The right tools free them for strategic work while reducing burnout.
Best Practices for Implementation
Implementing security automation requires a strategic approach to ensure effectiveness and avoid unintended risks. Following are five key best practices:
- Start with high-impact use cases – Focus automation on high-priority security tasks like malware detection, phishing response, and vulnerability management.
- Integrate automation with existing security tools – Ensure seamless compatibility with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), SOAR, firewalls, and identity access management (IAM) solutions.
- Define clear security playbooks – Establish predefined rules and workflows to guide automated threat responses.
- Use AI & Machine Learning for advanced threat detection – Leverage AI-driven security analytics to enhance accuracy and reduce false positives.
- Continuously monitor and optimize – Regularly audit automated security processes to improve performance and adapt to evolving threats.
How Forescout Helps
Forescout’s security automation solutions provide organizations with real-time visibility, automated threat response, and compliance enforcement, ensuring continuous protection against cyber threats. In fact, the Forescout Platform was the industry’s first automated cyber security platform that continuously manages the risk posture of assets across an enterprise’s digital terrain, providing complete coverage of IT, OT, IoT, and IoMT devices.
With Forescout’s security automation, organizations can proactively reduce cyber risk, accelerate threat response, and optimize security operations and playbooks — all while reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Forescout helps with security automation via:
- AI-Driven Risk Prioritization – Uses machine learning and advanced analytics to identify high-risk threats and prioritize remediation efforts.
- Automated Compliance Assessment and Enforcement – Continuously assesses the security posture and compliance of connected assets against internal policies, external standards, and industry regulations to ensure devices adhere to established security requirements and playbooks.
- Device Discovery and Risk Management: Automatically identifies and assesses devices across IT, IoT, OT, and IoMT environments, providing comprehensive visibility into the entire network, enabling organizations to understand their attack surface’s potential vulnerabilities and take action to remediate.
- Multi-Vendor Integration: Works with over 250 ISVs to harmonize security workflows, allowing different security tools, including SIEMs, to communicate and take coordinated actions.
- Network Access Control (NAC): Can automatically detect non-compliant devices and either prevent them from joining the network or shut down switch ports if a non-compliant device is connected.
- Regulatory Compliance Automation: Ensures continuous compliance with ISO 27001, NIST, GDPR, HIPAA, and other industry standards.
- Security Automation & Orchestration: Uses predefined workflows and playbooks to enforce policies and accelerate response actions, and orchestrate tasks, such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, and endpoint security configuration.
- Seamless Security Integration: Works across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments to unify security operations.
- Threat Detection and Response: Instantly detects and mitigates threats by continuously monitoring device behavior, posture, and compliance.
Experience a personalized demonstration to see how Forescout continuously discovers, assesses, and governs all your cyber assets, including IT, IoT, OT/ICS and IoMT, from campus to cloud to data center to edge.
[i] IBM (2024). Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024. Accessed March 21, 2025 from the following source: https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach
[ii] Ibid.