Dray:Break
Breaking Into DrayTek Routers Before Threat Actors Do It Again
In 2024, routers are a primary target for cybercriminals and state-sponsored attackers – and are the riskiest device category on networks. With this knowledge, we investigated one hardware vendor, DrayTek, with a history of security flaws to help it address its issues and prevent new attacks — especially when the risk of ransomware and denial of service attacks are so high today.
Learn what makes them vulnerable, the threat impact – and how to mitigate, today.
75%
in Commercial Networks
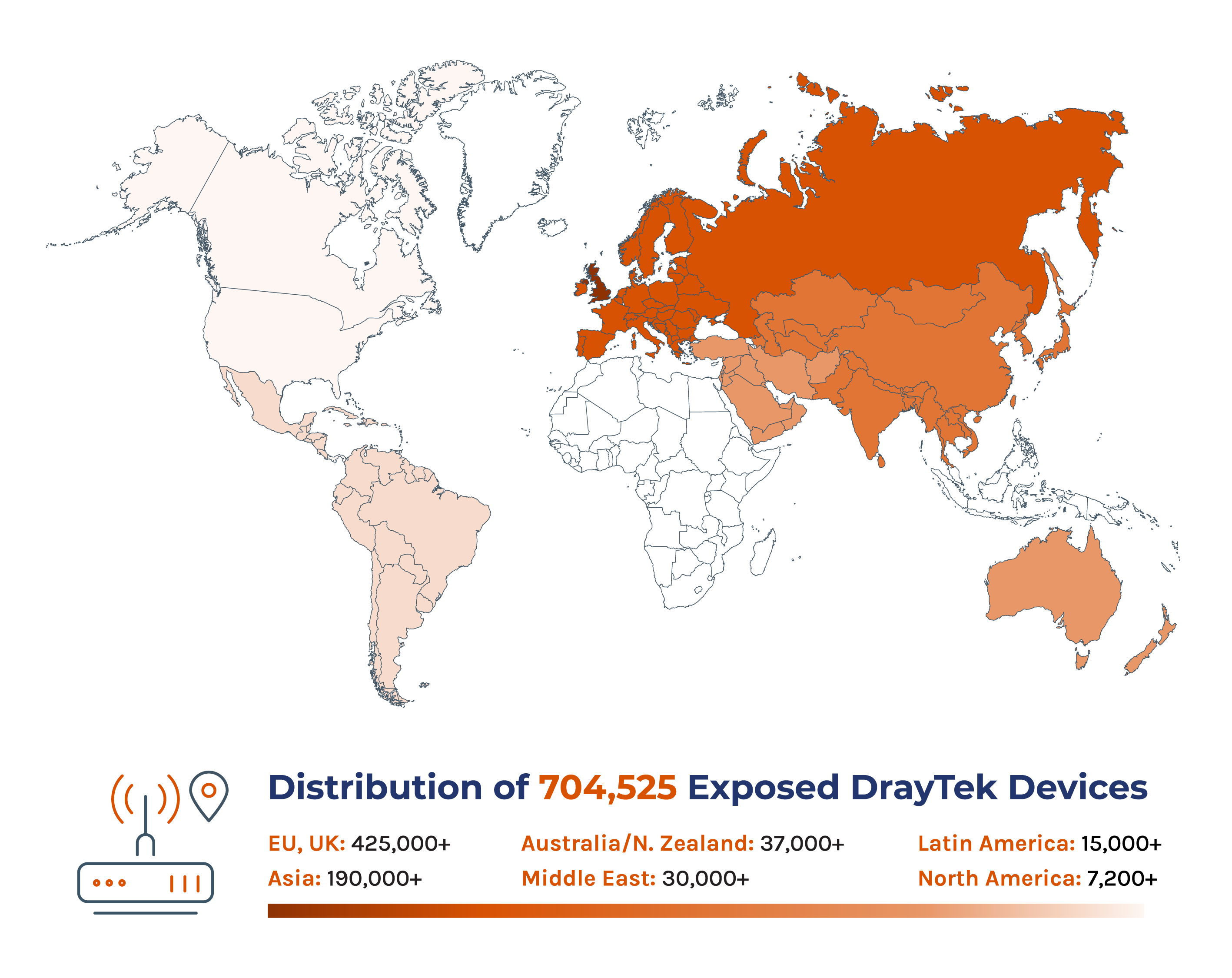
Where Are the Most Exposed Routers?
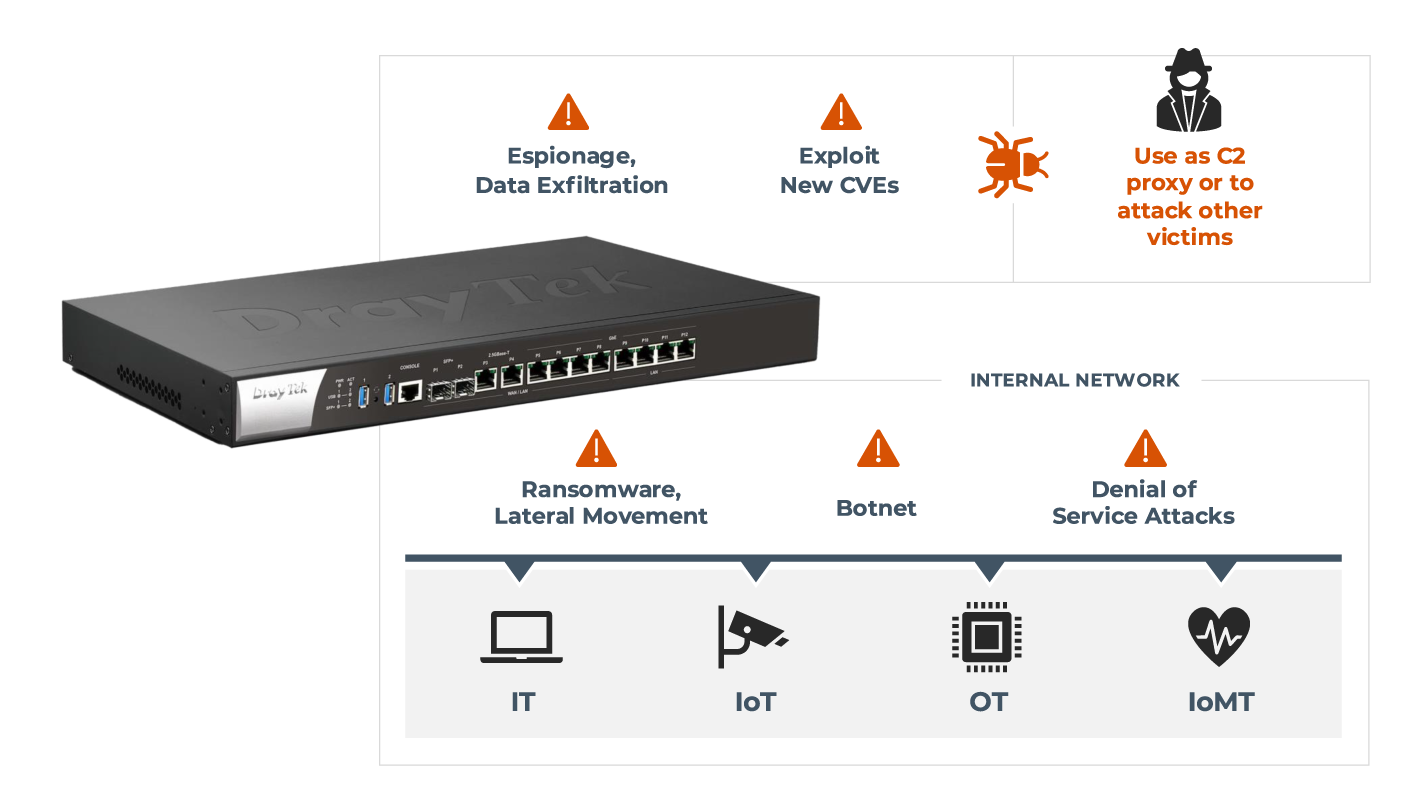
Attack Scenarios
See the potential attack scenarios involving a vulnerable device configured to expose the Web UI over the WAN (internet). The impact? A rootkit that survives reboots and firmware updates. Network traffic is intercepted to harvest credentials and sensitive data. The ability to pivot to devices on the local network for ransomware attacks or DoS.
Status of Routers: End of Life / End of Sale
Of the 704,000+ routers exposed to the internet, the majority (63%) are either End of Life (EoL) or End of Sale (EoS). What’s more, 24 device models are affected by the new vulnerabilities, including 11 that are EoL. This is troublesome given many manufacturers stop security patches and updates at this stage of the product lifecycle.
Support Status for Exposed Routers
Intended Use of Exposed Routers
FAQ: Dray:Break – DrayTek Routers Vulnerability Research Disclosure
What is DrayBreak?
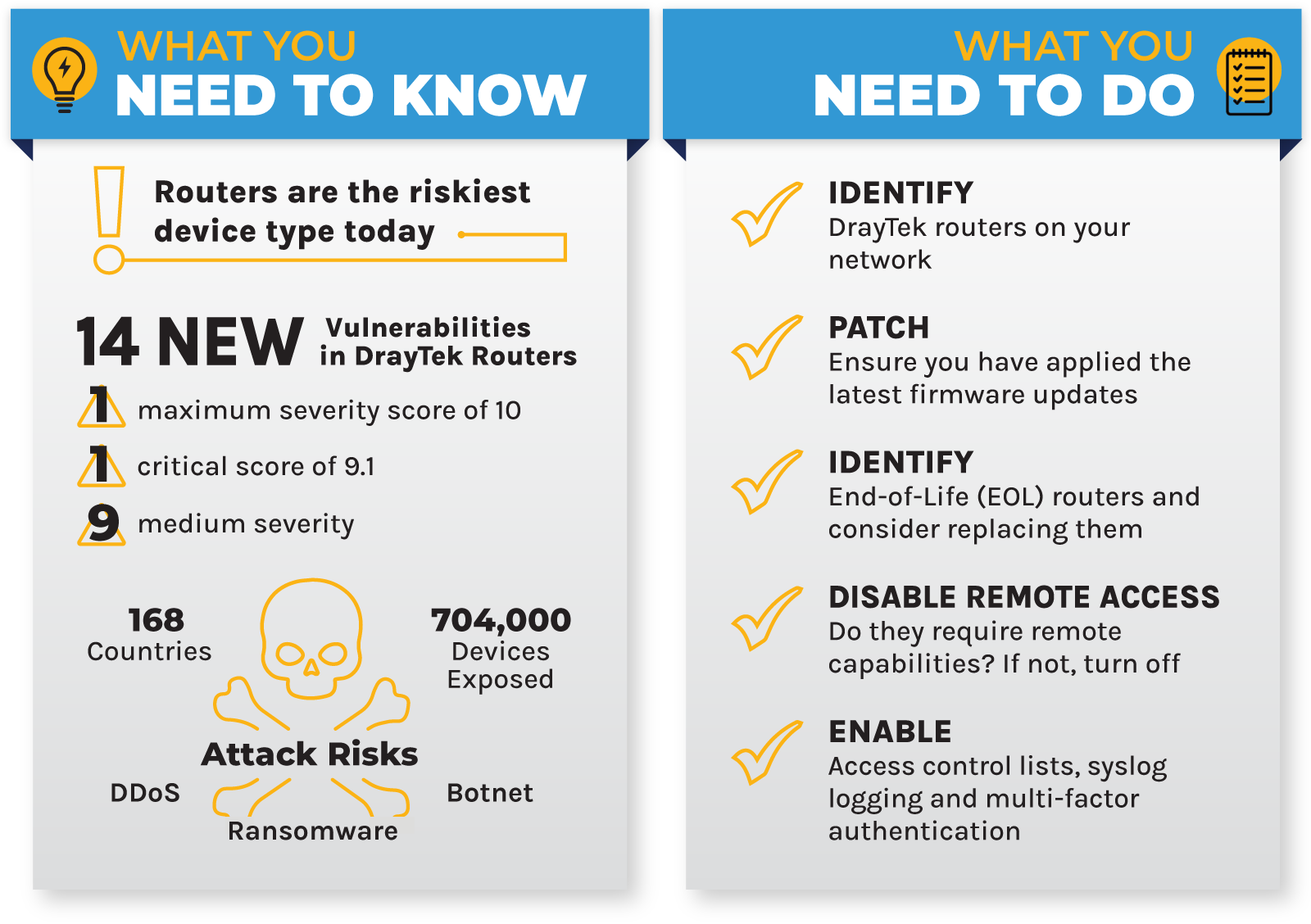
DrayBreak is a collection of 14 newly discovered vulnerabilities in popular residential and enterprise routers manufactured by DrayTek disclosed by Forescout Research – Vedere Labs. These vulnerabilities are significant because threat actors, including cybercriminals and state-sponsored groups, often target network infrastructure devices, such as routers, for initial access and persistence. Identifying and fixing these issues helps prevent exploitation as zero-day vulnerabilities.
Where are DrayTek routers used?
Over 704,000 vulnerable DrayTek routers are exposed online across 168 countries. The UK accounts for 36% of these routers, followed by Vietnam with 17% and the Netherlands with 9%. Although many of the vulnerable devices are small residential routers, 75% are intended for business use. These affected devices are found in multiple sectors, including healthcare, retail, manufacturing, financial services, and government.
What is the impact of the vulnerabilities?
Of the 14 vulnerabilities, one has the highest severity score of 10, and another is rated at 9.1. Nine vulnerabilities have medium scores and three have low scores. These vulnerabilities may allow attackers to take control of a router by injecting malicious code, maintain persistence on the device and use it as an entry point into enterprise networks.
What can organizations do to mitigate the risk from these vulnerabilities?
Complete protection requires patching devices with the affected software. DrayTek has released firmware patches for all affected devices, as outlined in the table below:
| Device Model | Fixed versions | EoL? |
|---|---|---|
| Vigor1000B, Vigor2962, Vigor3910 | 4.3.2.8 and 4.4.3.1 | No |
| Vigor3912 | 4.3.6.1 | No |
| Vigor165, Vigor166 | 4.2.7 | No |
| Vigor2135, Vigor2763, Vigor2765, Vigor2766 | 4.4.5.1 | No |
| Vigor2865, Vigor2866, Vigor2915 | 4.4.5.3 | No |
| Vigor2620, VigorLTE200 | 3.9.8.9 | Yes |
| Vigor2133, Vigor2762, Vigor2832 | 3.9.9 | Yes |
| Vigor2860, Vigor2925 | 3.9.8 | Yes |
| Vigor2862, Vigor2926 | 3.9.9.5 | Yes |
| Vigor2952, Vigor3220 | 3.9.8.2 | Yes |
In addition to patching, DrayTek has recommended the following actions for previous similar vulnerabilities:
- If remote access is enabled on your router, disable it if not needed. Use an access control list (ACL) and two-factor authentication (2FA) if possible.
- Verify that no additional remote access profiles (VPN dial-in, teleworker or LAN to LAN) or admin users (for router admin) have been added and that no ACLs have been altered.
- Disable remote access (admin) and SSL VPN. Since the ACL does not apply to SSL VPN connections (Port 443), temporarily disable SSL VPN until the firmware is updated.
- Always back up your configuration before performing an upgrade.
- After upgrading, confirm that the web interface displays the new firmware version.
- Enable syslog logging to monitor for abnormal events.
- Always use secure protocols such as HTTPS for internet activity.
- Follow additional network security tips on DrayTek’s Knowledge Base
Where do I go for more information?
For more information on the vulnerabilities and mitigation strategies, please refer to our blog.
Strategic Recommendations:
How Forescout Can Help
- Risk and exposure management: Identify, quantify and prioritize cybersecurity risk. Start by discovering and assessing every connected asset to gain real-time awareness of your attack surface.
- Network security: Continuously monitor all connected assets to govern network access, using real-time traffic visibility to manage segmentation and dynamic control policies to mitigate and remediate risk.
- Threat detection and response: Detect, investigate and respond to true threats and incidents using threat detection and response capabilities to collect telemetry and logs, correlate attack signals, generate high-fidelity detections and enable automated responses.